Which is a type of carbohydrate apex – Apex carbohydrates, a fascinating class of biomolecules, occupy a central stage in the realm of biochemistry, captivating scientists and researchers with their unique properties and diverse applications. This discourse delves into the intricate world of apex carbohydrates, unraveling their molecular makeup, biological functions, and industrial significance.
As we embark on this journey, we will explore the structural intricacies of apex carbohydrates, from simple monosaccharides to complex polysaccharides. Their involvement in energy metabolism, structural support, and cellular communication will be meticulously examined. Furthermore, we will uncover their industrial applications, ranging from food additives to pharmaceutical formulations.
Apex Carbohydrates

Apex carbohydrates, also known as storage carbohydrates, are a class of carbohydrates that serve as the primary energy reserves in plants and animals. They are characterized by their high molecular weight, complex structure, and ability to be broken down into simpler sugars for energy production.
Molecular Structure and Chemical Properties
Apex carbohydrates are composed of long chains of monosaccharides, which are linked together by glycosidic bonds. The most common monosaccharides found in apex carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, and galactose. These monosaccharides can be arranged in linear or branched chains, resulting in different types of apex carbohydrates with varying structures and properties.
Apex carbohydrates are typically insoluble in water and have a high molecular weight, ranging from hundreds to thousands of Daltons. They are non-reducing sugars, meaning they do not react with Benedict’s reagent or Fehling’s solution.
Functions of Apex Carbohydrates

Apex carbohydrates play multifaceted roles in living organisms, serving as the primary source of energy, providing structural support, and facilitating cell signaling. Their diverse functions are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and overall organismal health.
Energy Metabolism
Apex carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for cells. Through the process of glycolysis, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, releasing energy in the form of ATP. This ATP serves as the cellular energy currency, powering various cellular processes such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis.
Structural Support
Certain apex carbohydrates, such as cellulose and chitin, provide structural support to cells and tissues. Cellulose, found in plant cell walls, provides rigidity and strength, while chitin, found in the exoskeletons of insects and cell walls of fungi, offers protection and support.
Cell Signaling
Apex carbohydrates are involved in cell signaling processes. For instance, glycoproteins, carbohydrates attached to proteins, play a crucial role in cell-cell recognition, immune responses, and hormone signaling. These carbohydrates interact with specific receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering intracellular signaling cascades that regulate cellular activities.
Classification of Apex Carbohydrates

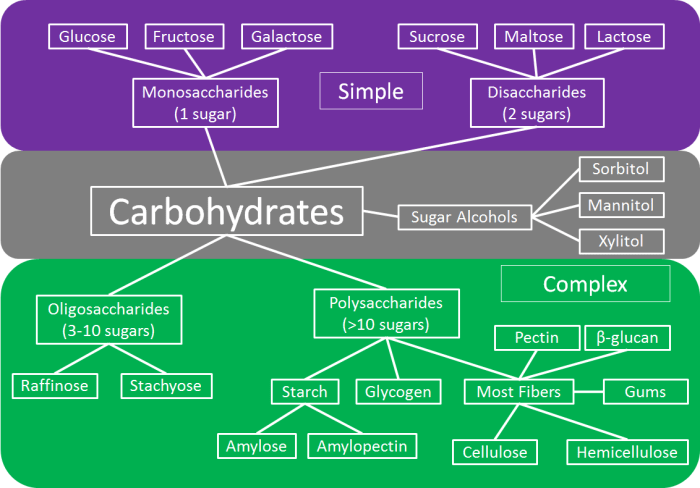
Apex carbohydrates, a type of carbohydrate, can be classified based on their structural complexity, which ranges from simple monosaccharides to complex polysaccharides. This classification system provides a framework for understanding the different types of apex carbohydrates and their varying properties.
The following table categorizes apex carbohydrates based on their structural complexity:
| Category | Structural Complexity | Examples | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monosaccharides | Single sugar units | Glucose, fructose, galactose | Simplest form of carbohydrates, cannot be broken down further |
| Disaccharides | Two monosaccharides linked together | Sucrose, lactose, maltose | Composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond |
| Oligosaccharides | A few (2-10) monosaccharides linked together | Raffinose, stachyose, fructooligosaccharides | Short chains of monosaccharides, typically found in plants |
| Polysaccharides | Many monosaccharides linked together | Starch, cellulose, glycogen | Complex carbohydrates composed of long chains of monosaccharides |
Metabolism of Apex Carbohydrates
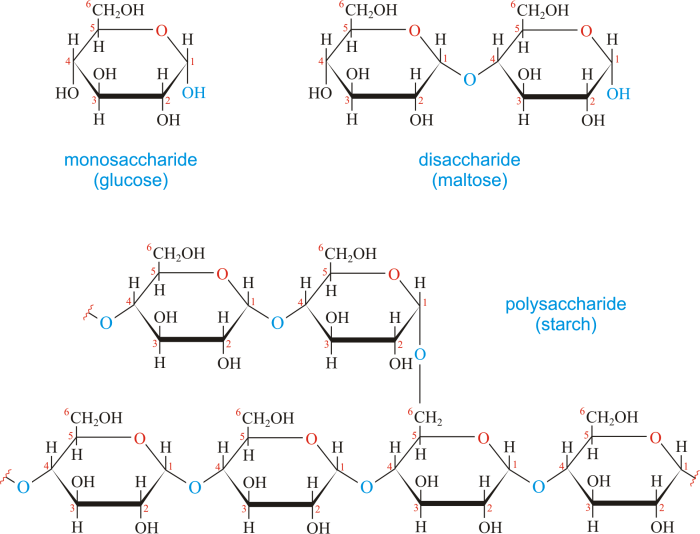
Apex carbohydrates, a type of polysaccharide, undergo a series of metabolic processes to be digested, absorbed, and utilized by the body. These processes involve the breakdown of complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, which can then be used for energy production or stored for later use.
Enzymes and Hormones Involved
The digestion of apex carbohydrates begins in the mouth, where the enzyme salivary amylase breaks down starches into smaller polysaccharides. In the stomach, gastric juices further break down these polysaccharides into smaller fragments. The majority of apex carbohydrate digestion, however, occurs in the small intestine.
Here, the enzyme pancreatic amylase further breaks down polysaccharides into disaccharides, which are then broken down into monosaccharides by the enzymes maltase, sucrase, and lactase.
The absorption of monosaccharides occurs primarily in the small intestine. Glucose and galactose are absorbed by active transport, while fructose is absorbed by facilitated diffusion. Once absorbed, monosaccharides are transported to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. The liver plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis, regulating blood glucose levels and converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage.
Role in Glucose Homeostasis and Energy Production
Apex carbohydrates play a vital role in glucose homeostasis. After a meal, the breakdown of apex carbohydrates into monosaccharides leads to an increase in blood glucose levels. This triggers the release of insulin from the pancreas, which promotes the uptake of glucose by cells for energy production or storage as glycogen.
In between meals, when blood glucose levels drop, the liver releases stored glycogen back into the bloodstream to maintain glucose homeostasis.
Monosaccharides derived from apex carbohydrates can be used directly for energy production through glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then further oxidized in the citric acid cycle to produce ATP, the body’s primary energy currency.
Applications of Apex Carbohydrates

Apex carbohydrates, a class of complex and branched polysaccharides, possess unique structural and functional properties that make them valuable in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
These applications span various sectors, including food, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology, where apex carbohydrates serve diverse purposes and offer numerous advantages.
In Food Industry, Which is a type of carbohydrate apex
- As thickening and gelling agents in sauces, soups, and desserts, apex carbohydrates provide texture and viscosity.
- In bakery products, they improve dough stability, increase loaf volume, and enhance crumb structure.
- As stabilizers in dairy products, they prevent syneresis and extend shelf life.
In Pharmaceuticals
- As drug delivery systems, apex carbohydrates can encapsulate and protect active ingredients, enabling targeted drug release.
- In wound healing, they promote tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation.
- As immune modulators, they enhance immune function and combat infections.
In Biotechnology
- As biomaterials, apex carbohydrates are used in tissue engineering, scaffolds, and drug delivery devices.
- In enzyme immobilization, they provide a stable matrix for enzymes, enhancing their activity and reusability.
- As prebiotics, they promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, supporting digestive health.
Essential Questionnaire: Which Is A Type Of Carbohydrate Apex
What are the primary functions of apex carbohydrates in living organisms?
Apex carbohydrates serve a multitude of biological roles, including energy provision, structural support, and cellular signaling. They are essential for cellular respiration, providing the body with readily available energy.
How are apex carbohydrates classified based on their structural complexity?
Apex carbohydrates are classified into four main groups based on their structural complexity: monosaccharides (single sugar units), disaccharides (two sugar units linked together), oligosaccharides (short chains of sugar units), and polysaccharides (long chains of sugar units).
What are some common industrial applications of apex carbohydrates?
Apex carbohydrates find extensive use in various industries. In the food industry, they are employed as sweeteners, thickeners, and stabilizers. In the pharmaceutical industry, they are used as excipients and drug delivery agents. Additionally, apex carbohydrates have applications in biotechnology, such as in the production of biofuels and bioplastics.