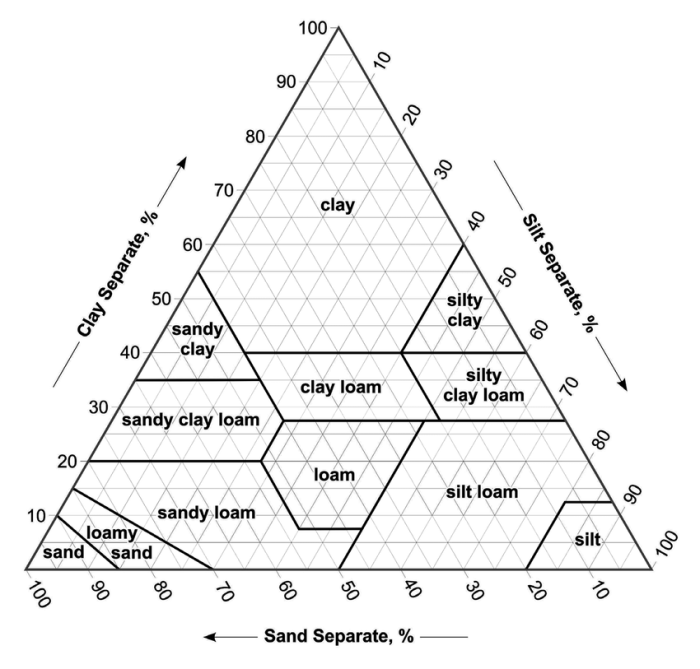
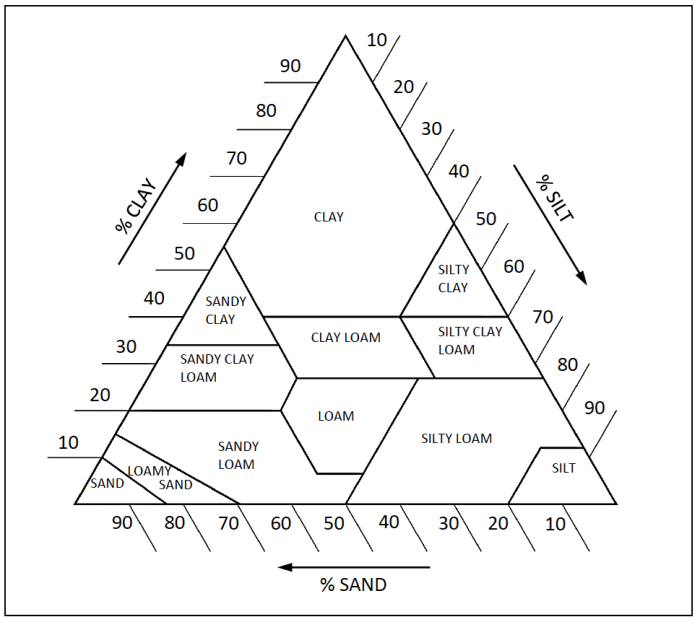
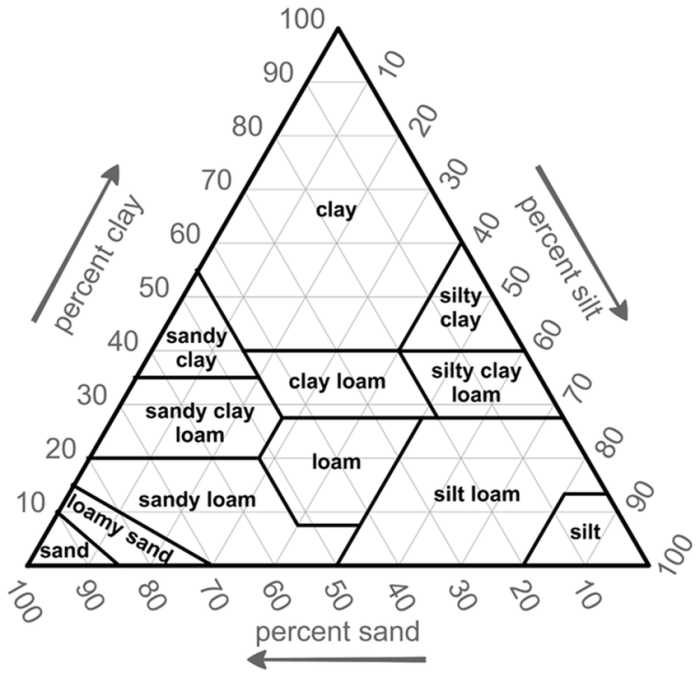
The soil texture triangle answer key provides a comprehensive understanding of soil composition and its impact on various aspects of soil management. This invaluable tool guides agricultural practices, soil classification, and water management strategies, making it an essential resource for farmers, soil scientists, and environmentalists alike.
Delving into the soil texture triangle, we unravel the intricacies of soil texture, its analysis, and its far-reaching applications. The triangle serves as a visual representation of the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles within a soil sample, enabling us to classify soils into distinct textural classes.
These classes, in turn, influence a multitude of soil properties, including water infiltration, water holding capacity, and nutrient availability, ultimately affecting plant growth and crop yields.
The Soil Texture Triangle
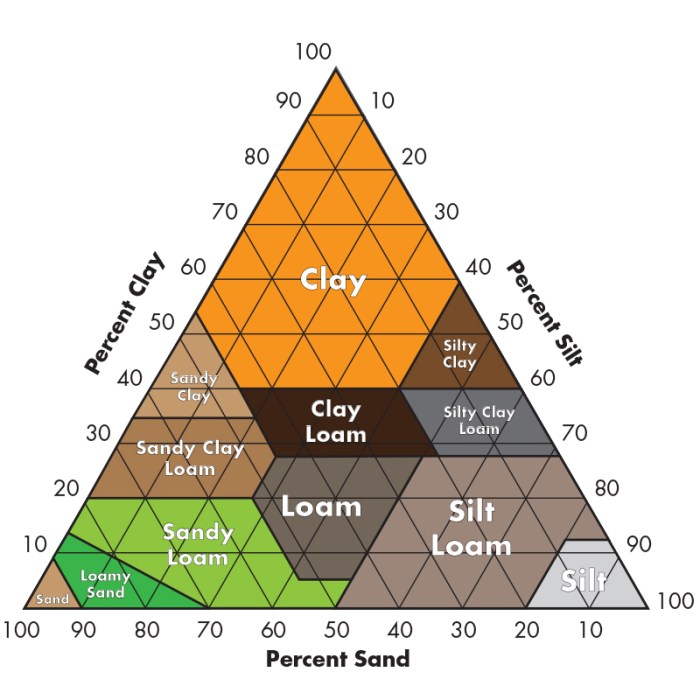
The soil texture triangle is a graphical representation of the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample. It is used to classify soils into different textural classes, which have implications for soil properties such as water infiltration, water holding capacity, and nutrient availability.
The triangle is divided into three main regions: the sand region, the silt region, and the clay region. The sand region is located at the top of the triangle and represents soils with a high proportion of sand particles. The silt region is located in the middle of the triangle and represents soils with a high proportion of silt particles.
The clay region is located at the bottom of the triangle and represents soils with a high proportion of clay particles.
The soil texture triangle is a useful tool for understanding soil properties and for making decisions about soil management practices.
Soil Texture Analysis, The soil texture triangle answer key
Soil texture analysis is the process of determining the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample. There are a number of different methods that can be used to analyze soil texture, but the most common method is the hydrometer method.
The hydrometer method involves dispersing a soil sample in water and then measuring the specific gravity of the suspension at different time intervals. The specific gravity of the suspension is used to calculate the percentage of sand, silt, and clay in the soil sample.
Importance of Soil Texture for Plant Growth
Soil texture has a significant impact on plant growth. Sandy soils have a low water holding capacity and are easily drained, which can make it difficult for plants to get the water they need. Silty soils have a higher water holding capacity than sandy soils, but they can be compacted easily, which can restrict root growth.
Clay soils have a very high water holding capacity, but they can be difficult to drain, which can lead to waterlogging.
The ideal soil texture for plant growth is a loam soil, which is a soil that contains a mixture of sand, silt, and clay. Loam soils have a good water holding capacity, they are well-drained, and they are easy to work.
Essential FAQs: The Soil Texture Triangle Answer Key
What is the purpose of the soil texture triangle?
The soil texture triangle is used to determine the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles in a soil sample, which helps in classifying soils into different textural classes.
How is soil texture determined?
Soil texture is determined by conducting a particle size analysis, which involves separating soil particles based on their size using methods such as sieving or sedimentation.
Why is soil texture important?
Soil texture influences various soil properties, such as water infiltration, water holding capacity, and nutrient availability, which are crucial for plant growth and crop production.