How is the amperage adjusted on a gma welder – Understanding how to adjust amperage on a GMA welder is crucial for achieving optimal weld quality. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the principles, factors, and techniques involved in adjusting amperage, empowering you to master this essential aspect of GMA welding.
Amperage plays a critical role in determining the heat input and penetration depth of the weld. By adjusting amperage appropriately, you can tailor the welding process to suit different materials, thicknesses, and joint configurations.
Understanding GMA Welding
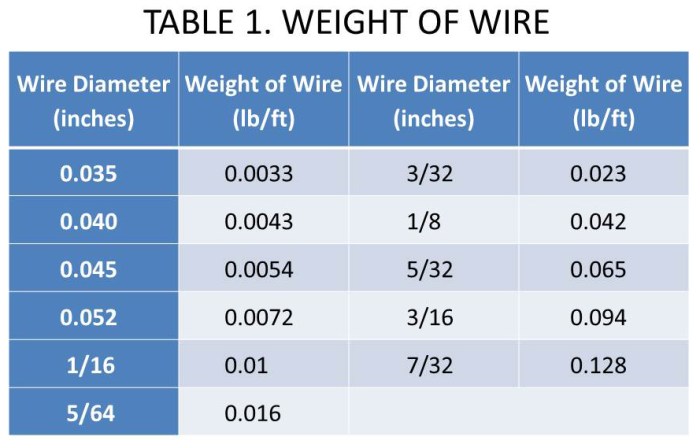
Gas Metal Arc (GMA) welding, also known as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, is a semi-automatic welding process that uses a continuously fed consumable wire electrode and an inert gas to shield the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
There are several types of GMA welding processes, including:
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
- Pulsed Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW-P)
- Short-Circuiting Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW-S)
Advantages of GMA welding include high deposition rates, versatility, and ease of use. However, it can also produce spatter and fumes, and requires proper shielding gas to prevent weld contamination.
Amperage Adjustment in GMA Welding: How Is The Amperage Adjusted On A Gma Welder
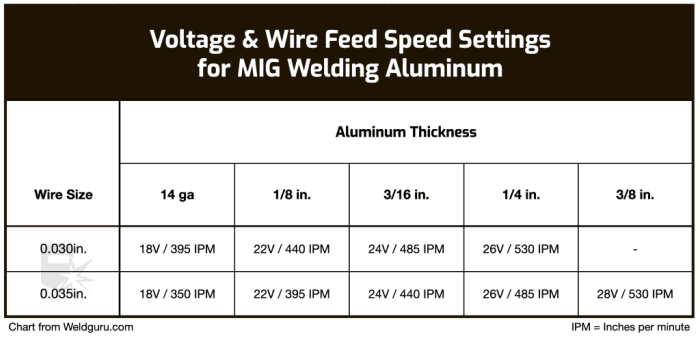
Amperage is a critical parameter in GMA welding that determines the heat input and penetration of the weld.
Factors that influence the optimal amperage setting include:
- Material thickness
- Joint design
- Welding speed
- Shielding gas composition
To adjust amperage on a GMA welder, follow these steps:
- Set the voltage to the recommended value for the material and wire diameter.
- Increase or decrease the amperage until the desired weld penetration and bead width are achieved.
- Monitor the weld pool and adjust amperage as necessary to maintain a stable and consistent weld.
Effects of Amperage on Weld Quality
Amperage directly impacts weld penetration, bead width, and shape.
- Higher amperage increases penetration but can also lead to burn-through.
- Lower amperage results in shallower penetration but can produce wider beads.
- Optimal amperage settings ensure a balance between penetration and bead width.
Amperage also affects weld strength and porosity.
- Insufficient amperage can lead to weak welds with lack of fusion.
- Excessive amperage can cause porosity and undercut.
- Proper amperage settings promote strong and sound welds.
Troubleshooting Amperage Issues
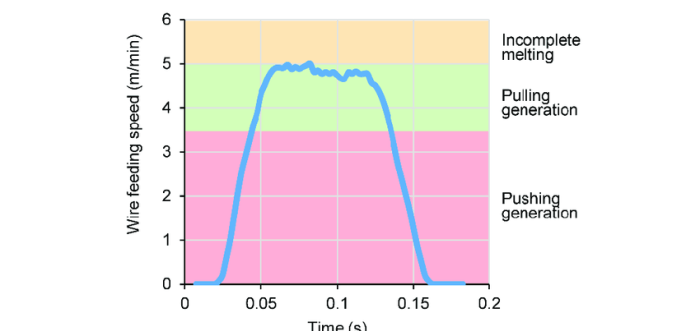
Common amperage-related problems in GMA welding include:
- Excessive spatter
- Lack of fusion
- Porosity
- Undercut
Troubleshooting tips for resolving amperage issues:
- Check the wire feed speed and adjust if necessary.
- Ensure proper shielding gas flow and composition.
- Inspect the welding torch and contact tip for damage or contamination.
- Calibrate the welding machine regularly.
Best Practices for Amperage Adjustment
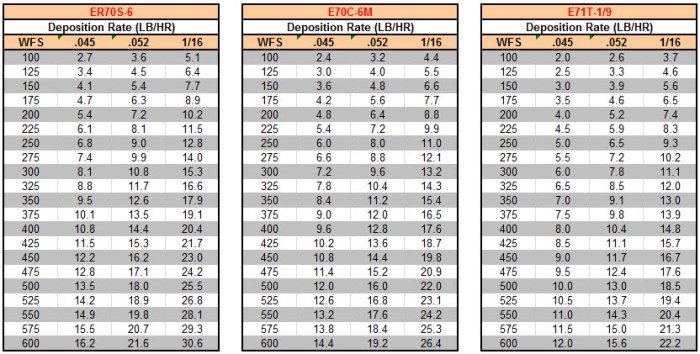
For optimal amperage adjustment, follow these tips:
- Use amperage meters or other tools to monitor amperage levels.
- Select the appropriate amperage setting based on the material, joint design, and welding conditions.
- Maintain consistent amperage throughout the welding process to ensure uniform weld quality.
- Refer to welding procedure specifications or manufacturer’s recommendations for specific amperage settings.
General Inquiries
What is the optimal amperage range for GMA welding?
The optimal amperage range varies depending on the material thickness, joint type, and desired weld penetration. Generally, thicker materials require higher amperage, while thinner materials require lower amperage.
How does amperage affect weld penetration?
Higher amperage increases weld penetration by providing more heat input. This is beneficial for welding thicker materials or achieving deep penetration in critical applications.
What are the consequences of excessive amperage?
Excessive amperage can lead to burn-through, excessive spatter, and weakened welds. It can also damage the welding equipment.