Network diagrams are the preferred technique for showing activity sequencing. – Network diagrams are the preferred technique for showing activity sequencing, providing a clear and concise visual representation of the tasks and their dependencies. They are widely used in project management, operations research, and other fields to plan and optimize complex activities.
Network diagrams offer several advantages over other methods of activity sequencing. They are easy to understand and interpret, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp the overall flow of activities. They also facilitate the identification of critical paths, bottlenecks, and potential delays, enabling project managers to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Network Diagrams as a Technique for Activity Sequencing
Network diagrams are widely recognized as the preferred technique for visualizing and sequencing activities in a project or process. They offer a clear and comprehensive representation of the tasks involved, their dependencies, and the overall flow of the project.
Benefits of Network Diagrams
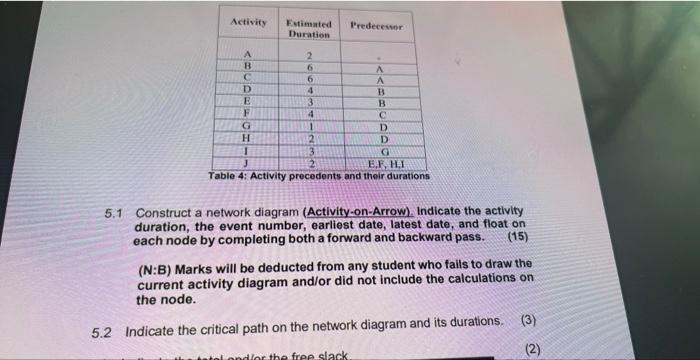
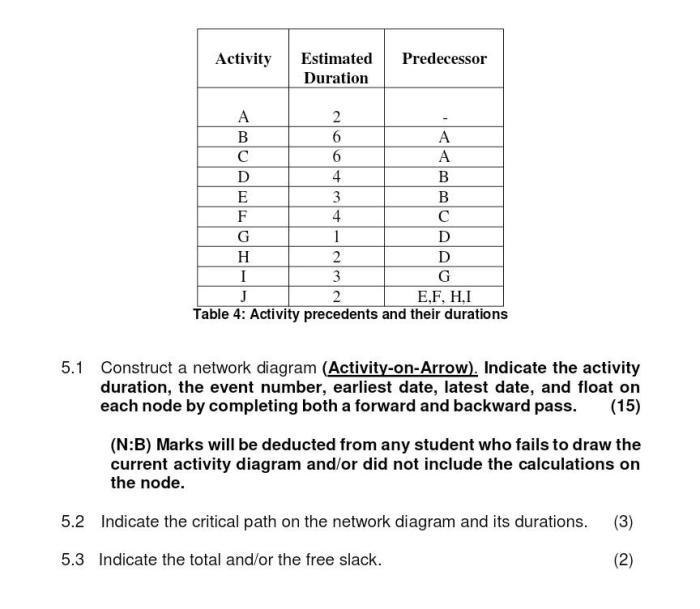
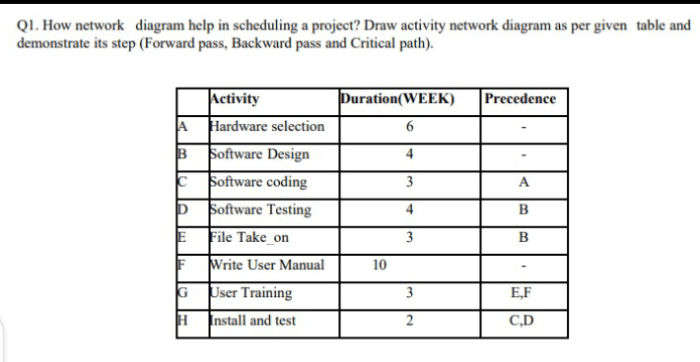
- Enhanced visualization: Network diagrams provide a graphical representation of the project, making it easier to understand the sequence of activities and their interrelationships.
- Improved planning: By mapping out the activities and their dependencies, network diagrams help project managers identify potential bottlenecks and optimize the project schedule.
- Efficient resource allocation: Network diagrams facilitate resource allocation by showing which activities require resources and when, enabling project managers to plan for resource utilization effectively.
- Enhanced communication: Network diagrams serve as a common language for project stakeholders, allowing them to visualize the project plan and understand the sequence of activities.
Types of Network Diagrams
- Activity-on-node (AON) diagrams: In AON diagrams, activities are represented by nodes, and the arrows connecting the nodes indicate the dependencies between activities.
- Activity-on-arc (AOA) diagrams: In AOA diagrams, activities are represented by arrows, and the nodes indicate the events that mark the start or completion of activities.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: Network diagrams are easy to understand, provide a comprehensive view of the project, and facilitate collaboration among stakeholders.
- Disadvantages: Network diagrams can become complex for large projects, and they may not always be suitable for projects with uncertain or dynamic dependencies.
- Nodes: Nodes represent activities or events in the project.
- Edges: Edges, also known as arrows or arcs, connect nodes and indicate the dependencies between activities.
- Labels: Labels are used to identify activities, durations, and other relevant information on the nodes and edges.
- Activity duration: Activity durations are typically represented by numbers placed on the edges connecting nodes.
- Dependency types: Different types of dependencies, such as finish-to-start (FS) or start-to-start (SS), are indicated by specific symbols or notations.
- Critical path: The critical path is highlighted using a different color or line style to indicate the sequence of activities that determines the overall project duration.
- Identify activities: Determine the activities that need to be completed as part of the project.
- Establish dependencies: Identify the dependencies between activities, such as which activities must be completed before others can start.
- Estimate activity durations: Determine the estimated time required to complete each activity.
- Draw the network diagram: Using the identified activities, dependencies, and durations, draw the network diagram using appropriate software or online tools.
- Microsoft Project: A widely used project management software that includes features for creating network diagrams.
- GanttPRO: An online project management tool that offers network diagramming capabilities.
- Lucidchart: A web-based diagramming tool that allows users to create network diagrams.
- Critical path analysis: Network diagrams help identify the critical path, which is the sequence of activities that determines the overall project duration. By focusing on the critical path, project managers can prioritize activities and mitigate potential delays.
- Bottleneck identification: Network diagrams can reveal bottlenecks, which are activities that hinder the progress of the project. By identifying bottlenecks, project managers can allocate additional resources or adjust the project schedule to address them.
- Delay analysis: Network diagrams enable project managers to analyze the impact of delays on the project completion date. By simulating different delay scenarios, they can develop contingency plans and mitigate risks.
- Construction projects: Network diagrams are commonly used in construction projects to plan and sequence activities, such as excavation, foundation work, and building construction.
- Software development projects: In software development, network diagrams are used to represent the dependencies between different modules and tasks involved in the development process.
- Manufacturing processes: Network diagrams are employed in manufacturing to optimize production processes by identifying dependencies between different production steps and machines.
- Resource allocation: Network diagrams can be used to allocate resources to activities, ensuring that the required resources are available when needed.
- Resource leveling: Resource leveling techniques can be applied to network diagrams to optimize resource utilization and minimize resource conflicts.
- Scheduling with uncertain durations: Network diagrams can be used to incorporate uncertainty into project scheduling by using probabilistic or simulation techniques.
- Project crashing: Advanced techniques can be used to identify activities that can be shortened to reduce the overall project duration.
- Multi-project scheduling: Network diagrams can be used to coordinate and schedule multiple projects, taking into account resource constraints and dependencies.
- Overly complex diagrams: Avoid creating overly complex network diagrams that are difficult to understand and maintain.
- Lack of clarity: Ensure that the network diagram is clear and easy to interpret, using consistent notation and labeling.
- Inaccurate information: Ensure that the information in the network diagram, such as activity durations and dependencies, is accurate and up-to-date.
- Use clear and concise labels: Label nodes and edges with brief but informative descriptions to enhance understanding.
- Emphasize the critical path: Highlight the critical path using a different color or line style to draw attention to the most important activities.
- Keep it simple: Create network diagrams that are easy to read and navigate, avoiding unnecessary details or clutter.
- A network diagram of a construction project that clearly shows the sequence of activities, dependencies, and critical path.
- A network diagram of a software development project that effectively represents the dependencies between different modules and tasks.
- A network diagram of a manufacturing process that optimizes production flow by identifying bottlenecks and resource constraints.
Elements of Network Diagrams for Activity Sequencing
Key Elements
Conventions and Standards, Network diagrams are the preferred technique for showing activity sequencing.
Creating Network Diagrams for Activity Sequencing

Steps Involved
Using Software and Online Tools
Using Network Diagrams for Activity Sequencing: Network Diagrams Are The Preferred Technique For Showing Activity Sequencing.
Analyzing and Optimizing
Examples of Use
Advanced Techniques in Network Diagrams for Activity Sequencing
Resource Allocation and Leveling
Examples of Advanced Applications
Best Practices for Network Diagrams in Activity Sequencing
Common Pitfalls
Tips for Effective Design
Examples of Well-Designed Network Diagrams
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key elements of a network diagram?
Network diagrams typically consist of nodes (representing activities), edges (representing dependencies), and labels (indicating activity durations and other relevant information).
How can network diagrams be used to identify critical paths?
By calculating the longest path through the network diagram, project managers can identify the critical path, which represents the sequence of activities that determines the overall project duration.
What are the advantages of using software or online tools to create network diagrams?
Software and online tools can automate the creation and analysis of network diagrams, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. They also offer advanced features such as resource allocation and leveling, which can further optimize activity sequencing.